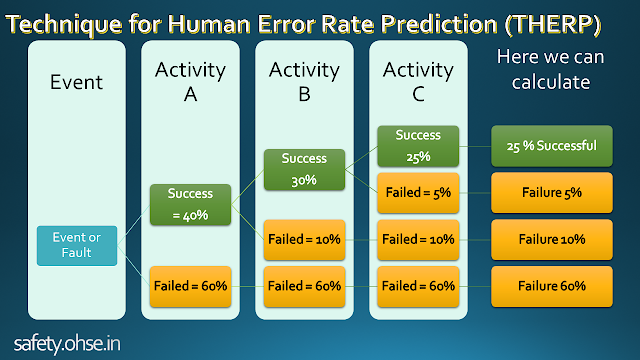
Technique for Human Error Rate Prediction (THERP)
Human Error Analysis recognizes and impacts possible human errors, or identifies the source of human errors found. The technique for human error-rate prediction (THERP) is a technique used in the human reliability assessment (HRA)
With the aim of eliminating errors, the Sandia Corporation created a tool to measure the probability of employee error in production operations.
The approach is based on the theory that it may be difficult or impossible to predict non-repetitive or infrequent acts, but it is possible to analyze repetitive actions to calculate human error probability data.
For selected tasks, THERP defines a Basic Error Rate (BER) that uses statistical methods to define valid human error rates when performing the task. The BER unit per million operations is a mistake.
This data on the rates of human failure is of interest to safety specialists. For Fault Tree Analysis(FTA) and Event Tree Analysis (ETA) it is useful. The data is a mean average and may not be applicable to the operator in question. Fewer errors can be made by professional operators.
STEPS OF THERP
- Define the system failures of interest.
- List and analyze the related Human operations.
- Estimate the relevant error probabilities.
- Estimate the effects of Human errors on the system failure events.
- Recommend changes to the system and recalculate the system failure probabilities.
ADVANTAGES OF THERP
- Easy to use
- Modest cost
- Tabulated values reduce need for Analyst judgment
- Selection rules reduce variability in results
- No specialized software needed
LIMITATIONS OF THERP
- Excessive emphasis on procedural details
- Detailed models mask true causes for errors
- False confidence that analyses are very precise
- No structured input from Plant Personnel
- Limited use for understanding important issues and
- recommending improvements




0 Comments
Comment your doubt or opportunity to improve